See Part One here
While Harry Richman and Dick Merrill waited comfortably at the home of T.W. Abbot for the necessary supplied and equipment to fix their aircraft, The Lady Peace, a modified Vultee V1-A, that had nosed down in a Musgrave Harbour bog on their return flight from Europe, a flurry of activity was happening at the Harbour Grace Airfield.
Once a popular airfield for those attempting to fly the Atlantic, the Harbour Grace Airfield had not been used as much since 1933. With construction starting on the airfield at Mile Post 314, what would become known as Gander, and a lack of funds, the future of the airfield was uncertain.
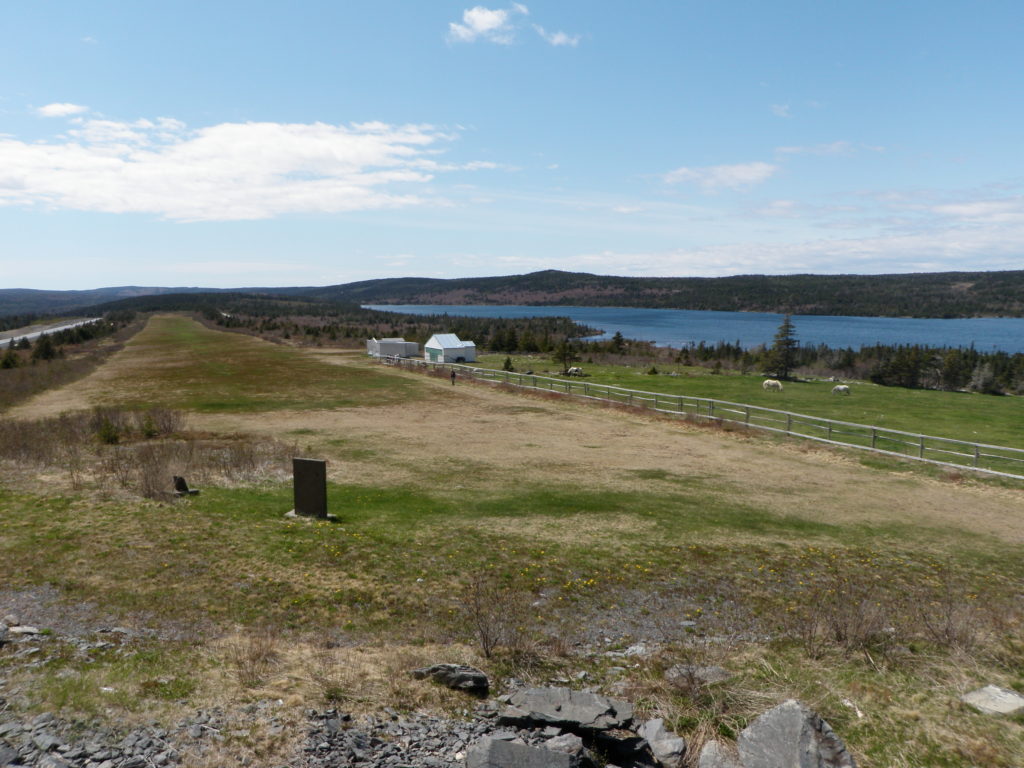

When The Lady Peace, with its two famous aviators, crashed in Musgrave Harbour, the Harbour Grace Airfield was suddenly very active. According to the airport log, four aircraft landed in Harbour Grace on 15 September 1936. The first was NC 16515, a Beechcraft scatterwing piloted by Duke Kranto, and owned by the Daily News in New York City. He landed in Harbour Grace at 12:35 local time, then left for Musgrave Harbour at 3:30, stayed in Musgrave Habour for three hours before flying back to Harbour Grace. Kranto stayed the night, and left for New York City at 8am on 16 September. Two other Beechcraft are listed as landing on 15 September: NC 15812 piloted by Carl O. Chader, and owned by O.J. Whitney Inc. Flying Service, and NC 15849, piloted by John H. Shobe and owned by Shobe Airlines Inc. These aircraft landed at 2pm and 2:30 respectively, and left at 8am the following morning. All three are listed as leaving at the same time, so it is assumed they left one after the other. The later two aircraft brought newspapermen to Harbour Grace, who then went to Musgrave Harbour.
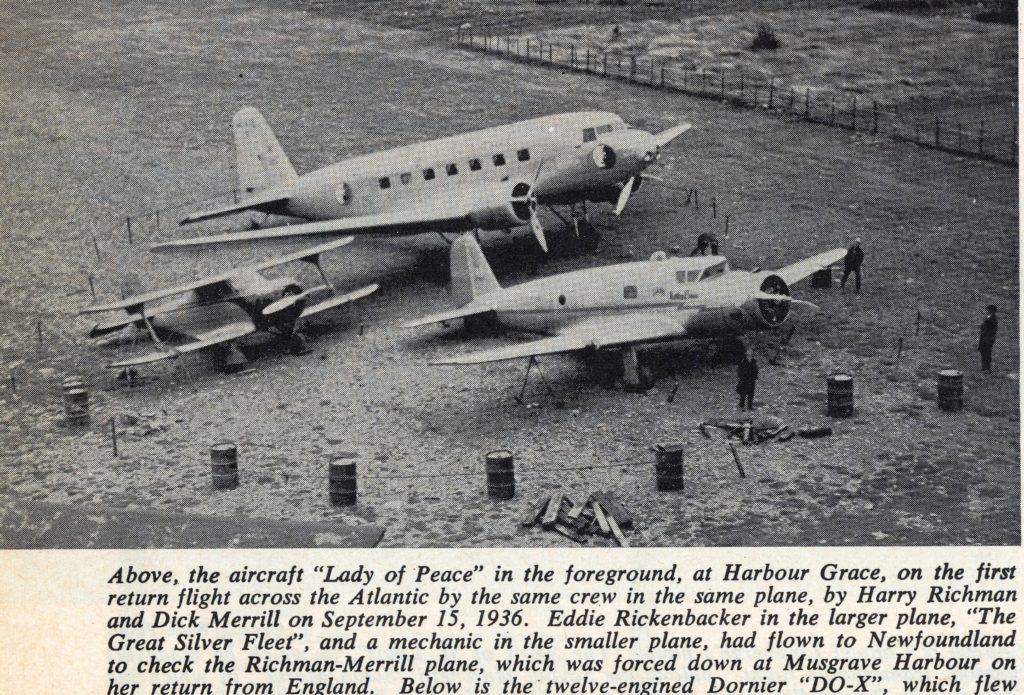
The largest plane to ever land in Harbour Grace also arrived on 15 September 1936. The Great Silver Fleet, NC 17731, owned by Eastern Air Lines, landed amongst the smaller Beechcraft. This aircraft was piloted by George W. Branson, co-piloted by Joe Kelly, and brought the famous Captain Eddie Rickenbacker to Newfoundland.

There was actually a fourth scatterwing that landed in Harbour Grace but wasn’t recorded in the log. The other newspaper aircraft left on 16 September, but a picture of The Lady Peace and The Great Silver Fleet available on the Digital Archives Initiative at MUN shows another Beechcraft. Further readings have not allowed me to identify the aircraft. The log indicates all of the newspaper aircraft had left on 16 September, and The Lady Peace did not arrive until the 18th. The only other possibility is that it was flown by one of the mechanics brought by Rickenbaker as suggested by Pushie (1959), even though the three mechanics, the pilot, co-pilot, and Rickenbacker could all comfortably fit on The Great Eastern Fleet, a DC-2. Perhaps Rickenbacker brought a small aircraft to possibly fly to Musgrave Harbour if needed? I am open to suggestions or further reading suggestions.

On the evening of 16 September, Rickenbaker chartered a boat, Lincoln II, to take him, his crew, and supplies, to Musgrave Harbour. Meanwhile, the residents of Musgrave Harbour were preparing a runway for The Lady Peace. It was determined that the hard-packed sand revealed by low tide would make a suitable runway, and a series of wooden ramps were constructed to move the aircraft to the makeshift runway.
Four days after their surprise landing in Musgrave Harbour, Merrill and Richman took off from the beach with just enough fuel for the shot hop to Harbour Grace. Given the condition of the runway, they wanted the aircraft to weigh as little as possible, looking to fuel-up in Harbour Grace. The Lady Peace, landed in Harbour Grace at 7pm on 18 September 1936.

Rickenbacker looked on as, at 8am on 19 September, The Lady Peace took off from Harbour Grace. The aircraft landed at Floyd Bennett Field in New York, where the wheels edged off the runway and sank into the mud. The aircraft had to be towed off the runway.
Ironically, The Lady Peace later went to war as a light bomber operating out of Spain. The aircraft was renamed Capitan Haya and survived the war. It was scrapped in 1953.
In the aftermath of The Lady Peace event, Harbour Grace attempted to renew the airfield. The Harbour Grace Airport Trust Company did not charge for the use of the airfield, but rather relied on donations. With all of the media attention, letters were sent to the Universal New Reel, Paramount News, Fox News, Hearst Metrotone News, and The Daily News, asking for donations toward the upkeep of the runway, suggesting a $25 donation. This suggests that aircraft from each of these news sources landed in Harbour Grace, and perhaps the mystery Beechcraft was among them, although the aircraft was still present when the letter was sent. At least one $25 donation was received from the O.J. Whitney Flying Service, whose aircraft was flown by Carl Chader.
With work starting on the Newfoundland Airport in what would become Gander, Thomas M. McGrath wrote to the Airport Committee suggesting that the airfield continues to be useful even with the completion of the larger airfield. In the interim, McGrath suggests it could be of use to visiting aircraft, and after completion could be an alternative landing place. Keep in mind, this was before the construction of the Second World War airbases, making these the two major airfield on the island. McGrath suggested that Mr. E. L. Oke of the Airport Committee write to Mr. Manning, the Secretary for the Department of Public Unitilies and discuss repairs and maintenance to the airport. A visit to the Provincial Archives may uncover more related correspondences.

Merrill returned to Newfoundland about 40 years later and at a reception in his honour in Harbour Grace, and actually inquired after the man, Israel, who we first me at Man Point Marsh as the plane landed.
Sources
Anonymous
1976 We Treated Them As If They Were Residents of Our Community. Decks Awash, 5(6): 59.
Clarke, D.J.
2018 Stories From Our Shores: Musgrave Harbour and the Ping Pong Flight. The Western Star, 04 December 2018.
Guy, R.W.
1987 Ten Miles Apart in Space: Five Years Apart in Time. One a Vultee;
the Other a Hudson. The Newfoundland Quarterly, 83(1):
5.
Jessamine, B.
n.d. The Ping Pong Flight Project. The Ping Pong Flight, website, accessed 20 December 2018
Mann, R.S.
1936 Letter to Paramount News, 18 September 1936. On File: Conception Bay Museum.
1936 Letter to O.J. Whitney Inc., 02 October 1936. On File: Conception Bay Museum.
McGrath, T.M.
1936 Letter to E.L. Oke, 02 November 1936. On File: Conception Bay Museum.
Pushie, G.F.
1959 Atlantic Flights From Newfoundland. The Atlantic Advocate, 49(12): 77-86.
Radecki, A.
2015 From Glendale to London with Peace, Pingong Balls, and the Ritz. Vintage Air, website, accessed 04 May 2018.
Whiteway, L.
1971 The Story of Musgrave Harbour. The Newfoundland Quarterly, 68(2): 6-11.








 Buy Me a Coffee
Buy Me a Coffee